Local LLMs | RAG
Build a smart Q&A system using LangChain, ChromaDB, and Ollama to combine LLMs with real-time document retrieval.
KEYWORDS
Generative AI, LLMs, RAG Architecture, ChromaDB, LangChain, Ollama
Introduction
- In the era of large language models (LLMs), Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a powerful paradigm for combining the strengths of LLMs with external knowledge sources.
- This project demonstrates how to build a RAG application using Python, LangChain, and Chroma.
- The application enables users to query a database of documents and receive contextually relevant answers, complete with source references.
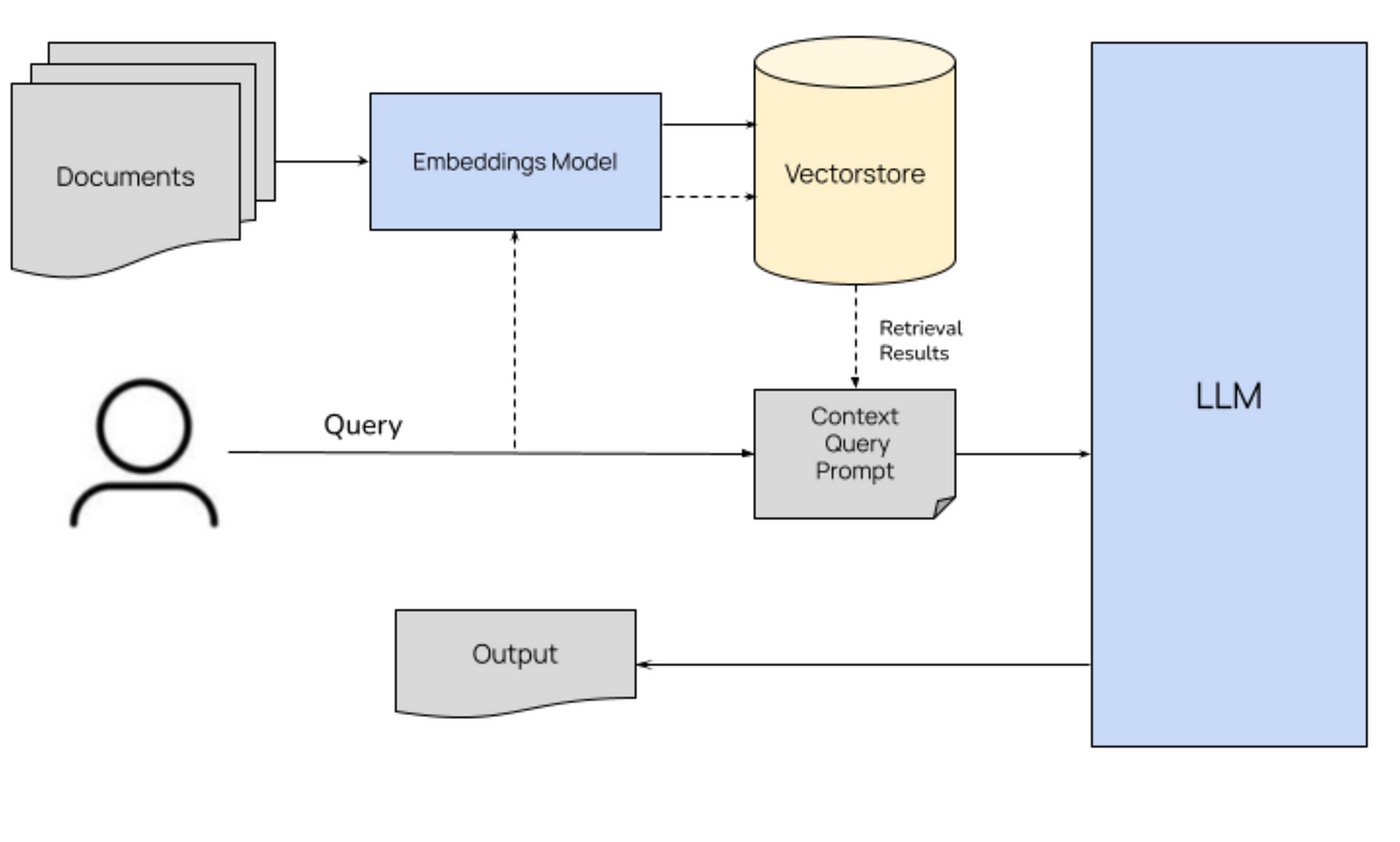 RAG architecture 1
RAG architecture 1
Background
- RAG applications enhance the capabilities of LLMs by integrating external knowledge bases.
- Instead of relying solely on the model’s pre-trained knowledge, RAG systems retrieve relevant information from a database and use it to generate accurate and context-aware responses.
- This approach is particularly useful for applications requiring up-to-date or domain-specific knowledge.
- Instead of relying solely on the model’s pre-trained knowledge, RAG systems retrieve relevant information from a database and use it to generate accurate and context-aware responses.
In this project, we use the following tools and libraries:
- LangChain framework for building applications powered by LLMs.
- Chroma vector database for storing and retrieving document embeddings.
- Ollama community-driven library for embeddings and LLMs.
Project Overview
The project consists of two main components:
- A script to load, process, and store documents in a Chroma vector database.
- A script to query the database and generate responses using a language model.
Key Features
- Automatically loads and processes PDF files from a specified directory.
- Splits documents into manageable chunks for efficient embedding and retrieval.
- Uses Chroma to perform similarity searches on document embeddings.
- Leverages the Ollama LLM to generate responses based on retrieved context.
Code Walkthrough
Database Population
The
populate_database.pyscript handles the ingestion and processing of documents. Key steps include:- Loading Documents:
- The
load_documentsfunction usesPyPDFDirectoryLoaderto load PDF files from thedatadirectory.
- The
- Splitting Documents:
- The
split_documentsfunction usesRecursiveCharacterTextSplitterto split documents into chunks of 800 characters with an overlap of 80 characters.
- The
- Storing in Chroma:
- The
add_to_chromafunction stores the document chunks in a Chroma vector database, ensuring no duplicate entries.
- The
- Loading Documents:
1
2
db.add_documents(new_chunks, ids=new_chunk_ids)
db.persist()
Query Interface
The query_data.pyscript provides a command-line interface for querying the database. Key steps include:- Embedding Search: The
query_ragfunction uses Chroma’ssimilarity_search_with_scoreto find the most relevant document chunks using cosine similarity:
- Embedding Search: The
- Prompt Construction: A custom prompt template integrates the retrieved context with the user’s query.
- LLM Response: The Ollama LLM generates a response based on the constructed prompt.
1
2
results = db.similarity_search_with_score(query_text, k=5)
response_text = model.invoke(prompt)
Embedding Function
The get_embedding_function.py script defines the embedding function using the OllamaEmbeddings model. This function is used for both storing and querying document embeddings.
Each document chunk is converted into a vector representation:
1
embeddings = OllamaEmbeddings(model="nomic-embed-text")
How It Works
- Run
populate_database.pyto load and process documents. Use the –reset flag to clear the database if needed. - Use
query_data.pyto ask questions. The script retrieves relevant context from the database and generates a response using the LLM.
Example Usage
- Populate the Database
1
python populate_database.py
- Query the Database
1
python query_data.py "What is the main topic of the document?"
Challenges and Learnings
Efficient Chunking: Splitting documents into meaningful chunks while preserving context is crucial for accurate retrieval.
- Overlapping chunks are calculated as:
- Embedding Quality: The choice of embedding model significantly impacts the performance of the vector search.
- Prompt Engineering: Crafting effective prompts is essential for generating high-quality responses from the LLM.
Conclusion
- This project showcases the power of RAG systems in building intelligent, context-aware applications.
- By combining LangChain, Chroma, and Ollama, we created a robust pipeline for document retrieval and question answering. The modular design ensures that the system can be easily extended and adapted to various use cases.